




Next: Final Form of Master
Up: Master Equation II: the
Previous: Thermal Bath Correlation Functions
Contents
Index
Let us have a closer look at the expressions
![$\displaystyle \hat{C}_{12}(z)=\int_0^{\infty}
d\omega {\rho(\omega) [1+n_B(\omega)}]
\int_{0}^{\infty}dt e^{-(z+i\omega)t}.$](img169.png) |
|
|
(41) |
The Laplace transform exists for Im to
ensure convergence of the integral, but in the
expressions above we need
to
ensure convergence of the integral, but in the
expressions above we need
 etc., i.e. purely imaginary arguments!
The limit
etc., i.e. purely imaginary arguments!
The limit
 , if explicitely written, reads
, if explicitely written, reads
![$\displaystyle \hat{C}_{12}(z=-i\Omega)=\lim_{t\to \infty}\int_0^{\infty}
d\omega {\rho(\omega) [1+n_B(\omega)}]
\int_{0}^{t}dt' e^{i(\Omega-\omega)t'}.$](img173.png) |
|
|
(42) |
Now,
![$\displaystyle \lim_{t\to \infty} \int_{0}^{t}dt' e^{i x t'}=\lim_{t\to\infty}
\...
...t}{x} + i \frac{1-\cos xt}{x}\right]=\pi \delta(x) +iP\left(\frac{1}{x}\right),$](img174.png) |
|
|
(43) |
where 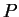 denotes the principal value.
denotes the principal value.
For the first term, we used a very useful
Theorem:
For any integrable, normalised function  with
with
 ,
,
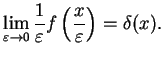 |
|
|
(44) |
Since
 , this yields the
Delta function above.
, this yields the
Delta function above.
We split the two bath correlation functions into real and imaginary parts,
Remarks:
- Real and imaginary parts of the correlation functions are
related to each other: Kramers-Kronig relations.
- Note the minus-sign in the definition of
 .
.





Next: Final Form of Master
Up: Master Equation II: the
Previous: Thermal Bath Correlation Functions
Contents
Index
Tobias Brandes
2004-02-18
![$\displaystyle \hat{C}_{12}(z)=\int_0^{\infty}
d\omega {\rho(\omega) [1+n_B(\omega)}]
\int_{0}^{\infty}dt e^{-(z+i\omega)t}.$](img169.png)
![$\displaystyle \hat{C}_{12}(z)=\int_0^{\infty}
d\omega {\rho(\omega) [1+n_B(\omega)}]
\int_{0}^{\infty}dt e^{-(z+i\omega)t}.$](img169.png)
![$\displaystyle \hat{C}_{12}(z=-i\Omega)=\lim_{t\to \infty}\int_0^{\infty}
d\omega {\rho(\omega) [1+n_B(\omega)}]
\int_{0}^{t}dt' e^{i(\Omega-\omega)t'}.$](img173.png)
![$\displaystyle \lim_{t\to \infty} \int_{0}^{t}dt' e^{i x t'}=\lim_{t\to\infty}
\...
...t}{x} + i \frac{1-\cos xt}{x}\right]=\pi \delta(x) +iP\left(\frac{1}{x}\right),$](img174.png)
![]() with
with
![]() ,
,
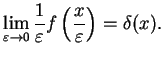
![]() , this yields the
Delta function above.
, this yields the
Delta function above.

