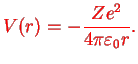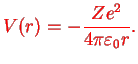Next: Orbital Angular Momentum
Up: Hydrogen Atom (non-relativistic)
Previous: Non-relativistic Single Particle Quantum
Contents
Index
The hydrogen atom therefore leads to a special case  of the solution of a stationary Schrödinger equation in the central potential
of the solution of a stationary Schrödinger equation in the central potential
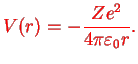 |
|
|
(1.6) |
Here,  is introduced in order to be able to later generalise from proton charge
is introduced in order to be able to later generalise from proton charge  to arbitrary charge
to arbitrary charge  . We use Dirac kets and write the stationary Schrödinger equation for
. We use Dirac kets and write the stationary Schrödinger equation for 
![$\displaystyle \hat{H} \vert\Psi\rangle = E \vert\Psi\rangle \leftrightarrow
\left[- \frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\Delta + V(r)\right] \Psi({\bf r}) = E \Psi({\bf r})$](img46.png) |
|
|
(1.7) |
with the Hamiltonian
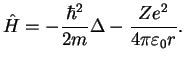 |
|
|
(1.8) |
Tobias Brandes
2005-04-26