




Next: Two-electron Atoms and Ions
Up: The Exchange Interaction
Previous: Perturbation Theory
Contents
Index
1. For
 the anti-symmetrical orbital state vanishes and one has
the anti-symmetrical orbital state vanishes and one has
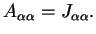 |
|
|
(2.27) |
In this case there is only one singlet state and there are no triplet states.
2. Extreme examples for the interaction potential:
Tobias Brandes
2005-04-26
