



Next: ** Generating Function (5-30
Up: The Harmonic Oscillator
Previous: Energies (2 min)
Contents
We introduce our `vector notation' (Dirac notation) from section 3, where the normalized
wave functions 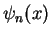 are denoted as
are denoted as 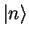 , because they are vectors
in a Hilbert space. In this problem, the
, because they are vectors
in a Hilbert space. In this problem, the 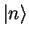 shall correspond to the normalized
wave functions of the one-dimensional harmonic oscillator of frequency
shall correspond to the normalized
wave functions of the one-dimensional harmonic oscillator of frequency 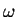 .
The
.
The 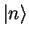 form an orthogonal system;
we write the scalar product as
form an orthogonal system;
we write the scalar product as
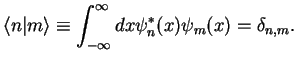 |
|
|
(33) |
1. Consider the state
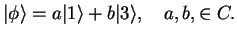 |
|
|
(34) |
Which condition must the coefficients 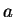 ,
,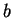 fulfill in order that
fulfill in order that
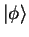 is normalized?
Write the normalization condition in the `abstract, elegant form', using
is normalized?
Write the normalization condition in the `abstract, elegant form', using
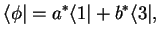 |
|
|
(35) |
as
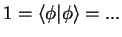
2. What is the probability to find the energy values 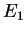 and
and 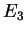 in an energy measurement
of a system in the state
in an energy measurement
of a system in the state
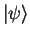 ?
?
3. Calculate the expectation value of the energy in the state
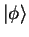 for general
for general
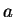 and
and 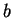 and for
and for
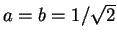 .
.




Next: ** Generating Function (5-30
Up: The Harmonic Oscillator
Previous: Energies (2 min)
Contents
Tobias Brandes
2004-02-04
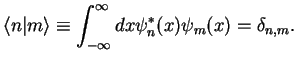
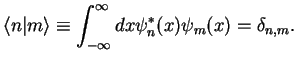
![]() and
and ![]() in an energy measurement
of a system in the state
in an energy measurement
of a system in the state
![]() ?
?
![]() for general
for general
![]() and
and ![]() and for
and for
![]() .
.