




Next: Literature
Up: Introduction
Previous: Formal Splitting
Contents
Index
1. `Simple' Systems with few degrees of freedom: typically
quantum optics systems, atoms, few-level systems, cavity modes.
- Weak coupling approximation: Master Equation (Born and Markov Approximation)
- Damped harmonic oscillator.
- Solution methods: phase-space methods (
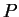 -representation etc.).
-representation etc.).
- Solution methods: quantum trajectories.
- Correlation Functions, Quantum Regression Theorem.
- Beyond weak coupling approximation: Feynman-Vernon influence functional (path integral) theories;
R. P. Feynman, F. L. Vernon, Ann. Phys. (N.Y.) 24, 118 (1963). Non-exponential
decay laws at low temperatures.
- Exact solution of damped harmonic oscillator.
- Spin-Boson Problem, Two-Level System.
- Non-Markovian versus Markovian, Lindblad versus non-Lindblad.
- `Non-standard' methods.
2. Systems with many degrees of freedom: typically condensed matter systems, electrons
+ phonons (particle statistics).
- Quasiclassical kinetic theories, Boltzmann equation.
- Quantum Many-Body Non-Equilibrium Methods. (Keldysh) Greens Function Methods, quantum
Boltzmann equation.
In this chapter, we will concentrate on 1. (`Simple' Systems with few degrees of freedom).
Also, not discussed in detail in this lecture are
- Nakajima-Zwanzig theories, Mori projection operator theories. These give a more formal
approach towards system-bath theories.
- `Early approaches' such as Wigner-Weisskopf theory of spontaneous emission.
- ...
Generally speaking, quantum dissipation can be regarded as
a subfield of non-equilibrium quantum statistics/ non-equilibrium many-body theory.





Next: Literature
Up: Introduction
Previous: Formal Splitting
Contents
Index
Tobias Brandes
2004-02-18