




Next: Coulomb Gauge
Up: Potentials
Previous: Potentials
Contents
Index
The potentials are not uniquely determined by the fields which are left invariant under a gauge transformation
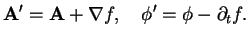 |
|
|
(1.14) |
Again in Fourier space,
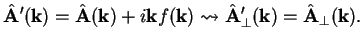 |
|
|
(1.15) |
The important transverse component of the vector potential, from which the transverse components
 and
and
 are derived via Eq. (VII.1.12), is therefore left invariant under a gauge transformation.
are derived via Eq. (VII.1.12), is therefore left invariant under a gauge transformation.
Tobias Brandes
2005-04-26