




Next: Pure Vibrational Dipole Transitions
Up: Pure Vibration
Previous: Pure Vibration
Contents
Index
The Hamiltonian of the harmonic oscillator
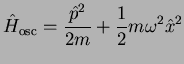 |
|
|
(2.6) |
can be re-written using the ladder operators
as
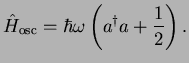 |
|
|
(2.9) |
The commutation relation is
![$\displaystyle [\hat{x},\hat{p}]=i\hbar,\quad [a,a^{\dagger}]=1.$](img1451.png) |
|
|
(2.10) |
The eigenfunctions of the harmonic oscillator are
 -phonon states,
-phonon states,
where
 are the Hermite polynomials.
are the Hermite polynomials.
The ladder operators are also called creation (
 ) and annihiliation
) and annihiliation
 operators. They act on the states
operators. They act on the states
 as
as
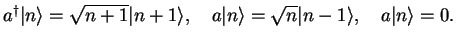 |
|
|
(2.12) |
The state
 is called ground state.
is called ground state.





Next: Pure Vibrational Dipole Transitions
Up: Pure Vibration
Previous: Pure Vibration
Contents
Index
Tobias Brandes
2005-04-26
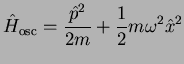
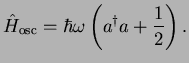


![]() ) and annihiliation
) and annihiliation
![]() operators. They act on the states
operators. They act on the states
![]() as
as