Next: Example: Two-Level System
Up: Time-Dependence in Quantum Mechanics
Previous: Time-Dependence in Quantum Mechanics
Contents
Index
(Set
 in the following). In this case, the initial value problem
in the following). In this case, the initial value problem
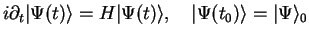 |
|
|
(1.6) |
is formally solved as
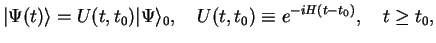 |
|
|
(1.7) |
where we introduced the time-evolution operator
 as
the exponential of the operator
as
the exponential of the operator
 by the power series
by the power series
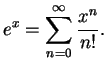 |
|
|
(1.8) |
Things are simple, however, when we use the solutions of the stationary Schrödinger equation
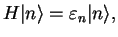 |
|
|
(1.9) |
where the eigenstates
 form a complete basis and one has
form a complete basis and one has
where the underlined terms are the expansion coefficients of
 in the basis
in the basis
 .
.





Next: Example: Two-Level System
Up: Time-Dependence in Quantum Mechanics
Previous: Time-Dependence in Quantum Mechanics
Contents
Index
Tobias Brandes
2005-04-26