




Next: -representation
Up: -representation
Previous: Solution of the PDE
Contents
Index
Since we know the solution for  , we perform a
transformation of variables and seek the solution for
, we perform a
transformation of variables and seek the solution for  in the form
in the form
![$\displaystyle P(z,z^*t)=F(u,u^*,s),\quad{u=ze^{+i\left[ \bar{\Omega} - i\kappa\right]t},
u^*=z^*e^{-i\left[ \bar{\Omega} + i\kappa\right]t},s=t},$](img376.png) |
|
|
(87) |
which leads to
where in the last line we compared with the original PDE. Therefore, one has
where we used
 ,
cf. Eq.(7.88). The big advantage now is that we had got rid of the
first order derivatives with the
,
cf. Eq.(7.88). The big advantage now is that we had got rid of the
first order derivatives with the  ,
, -dependent coefficients. Eq.(7.90) is now
a standard diffusion equation with time
-dependent coefficients. Eq.(7.90) is now
a standard diffusion equation with time  -dependent coefficients, which can be
solved by Fourier transformation:
-dependent coefficients, which can be
solved by Fourier transformation:
Reminder: Complex Fourier Transformation, cf (4.141)
Fourier Trafo 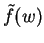 |
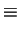 |
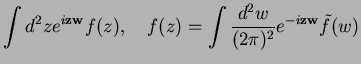 |
|
scalar product 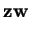 |
 |
![\begin{displaymath}\frac{1}{2}\left(zw^*+z^*w\right)=(z_1,z_2)\left(
\begin{array}[h]{c}
w_1\\ w_2
\end{array}\right)\end{displaymath}](img390.png) |
(90) |
Reminder: Gauß Integrals
We now Fourier-transform Eq.(7.90),
 , to obtain
, to obtain
Now we remember
![$ u=ze^{+i\left[ \bar{\Omega} - i\kappa\right]t}$](img404.png) ,
,
 , and write
, and write  in
in
 , to find
, to find
This is the solution of the initial value problem of the PDE:
we have explicitely constructed the propagator
 and expressed the solution
of the PDE at times
and expressed the solution
of the PDE at times  in terms of the initial
in terms of the initial 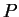 -distribution
-distribution
 .
.





Next: -representation
Up: -representation
Previous: Solution of the PDE
Contents
Index
Tobias Brandes
2004-02-18
![$\displaystyle \left(i \left[ \bar{\Omega} - i\kappa\right]ze^{+i\left[ \bar{\Om...
...ft[ \bar{\Omega} + i\kappa\right]t}
\partial_{u^*} +\partial_s\right)F(u,u^*,s)$](img378.png)
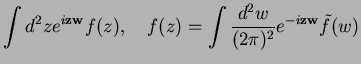
![\begin{displaymath}\frac{1}{2}\left(zw^*+z^*w\right)=(z_1,z_2)\left(
\begin{array}[h]{c}
w_1\\ w_2
\end{array}\right)\end{displaymath}](img390.png)




![]() , to obtain
, to obtain





![$\displaystyle \int d^2 z'\frac{1}{\pi n_B \left(1-e^{2\kappa t}\right)}
\exp\le...
...\right]t}-z'\vert^2}
{n_B \left(e^{2\kappa t} -1\right)}\right\} P(z',z'^*,t=0)$](img408.png)
![$\displaystyle \int d^2 z'\frac{1}{\pi n_B \left(1-e^{-2\kappa t}\right)}
\exp\l...
...pa\right]t}\vert^2}
{n_B \left(1-e^{-2\kappa t} \right)}\right\} P(z',z'^*,t=0)$](img409.png)

![$\displaystyle \frac{1}{\pi n_B \left(1-e^{-2\kappa t}\right)}
\exp\left\{-\frac...
...Omega} - i\kappa\right]t}\vert^2}
{n_B \left(1-e^{-2\kappa t} \right)}\right\}.$](img412.png)