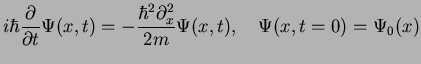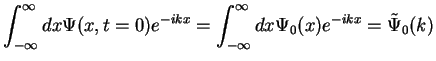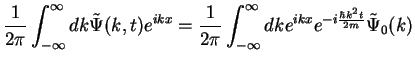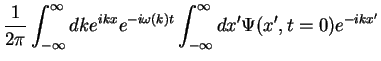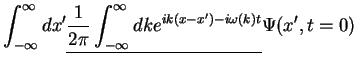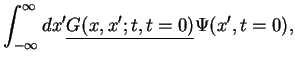Next: Position and Momentum in
Up: Fourier Transforms and the
Previous: The Delta Functional (`Delta
Contents
The Schrödinger equation for a free particle,
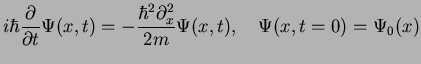 |
|
|
(53) |
can be solved by Fourier transformation:
The last equation is an ordinary differential equation in 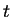 that can be solved easily:
that can be solved easily:
Here, the initial value
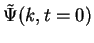 appears; it is given by our definition for the Fourier transform
appears; it is given by our definition for the Fourier transform
Therefore, if we know the initial wave function 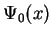 , we know its Fourier transform
, we know its Fourier transform
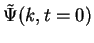 and can calculate the solution
and can calculate the solution 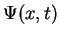 at a later time
at a later time 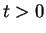 by Fourier back transformation,
by Fourier back transformation,
where we defined the propagator of the particle which propagates the wave function from its
initial form at 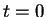 to its form at a later time
to its form at a later time 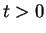 .
.




Next: Position and Momentum in
Up: Fourier Transforms and the
Previous: The Delta Functional (`Delta
Contents
Tobias Brandes
2004-02-04