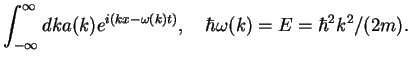Next: Math: Fourier Integral
Up: Introduction
Previous: The continuity equation
Contents
We had arrived at the Schrödinger equation starting from the wave packet
In the following, we formalize such superpositions of plane
plane waves by introducing the concept of Fourier integrals and the Fourier transform of a function.
The Fourier transform is a powerful tool to solve linear partial differential equations
such as the Schrödinger equation for a free particle (potential 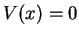 ).
).
Subsections
Tobias Brandes
2004-02-04